With cyberthreats constantly evolving, the need for effective cybersecurity solutions to safeguard sensitive infrastructures and data has never been more pressing.
The challenge is daunting: how can you effectively protect your infrastructures and their precious data? A new approach has emerged to meet this challenge, one that draws its strength from the collaboration of a community and the interconnection of cybersecurity solutions. This innovative strategy has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach cybersecurity, creating a united front against cyberattacks. In this article, we take an in-depth look at this technology and reveal how it works.
The power of collaboration
A collaborative approach to cybersecurity means that every user contributes to a shared database of malicious IP addresses, reinforcing collective security. The larger the community, the more robust and effective the protection offered. This diversity of data guarantees the quality of threat information, which is essential for accurate and timely detection.
This collaborative approach allows information on new threats to be shared rapidly, enabling all members of the community to protect themselves against these threats as soon as they are discovered. This information is then used to populate a database called blocklist.
The blocklist is a list of IP addresses that have been identified as malicious by the community. It is constantly updated with new information from the community. So every time a member detects a new threat, this information is added to the blocklist, enabling all other community members to protect themselves against it. It is this collaboration and sharing of information that is the strength of this approach.
The importance of behavioral analysis
Behavioral analysis plays a crucial role in threat detection. By analyzing logs and requests, we can identify malicious behavior and block the associated IP addresses. This proactive approach enables threats to be detected and neutralized before they cause any damage. In addition, behavioral analysis can detect threats that are not yet known, as it focuses on behavior rather than specific threat signatures.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
An Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) is an essential security solution that continuously monitors and analyzes network or system traffic to detect suspicious or malicious activity and take action against it. It is an essential first line of defense against cyber threats. The basic function of an IDPS is to monitor network traffic for abnormal or suspicious behavior. This can include a variety of activities, from unauthorized intrusion attempts, such as brute-force attacks, to potentially malicious behavior, such as port scans or attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities.
When an IDPS detects suspicious activity, it takes steps to respond. These measures can vary depending on the severity of the threat and the system configuration, but can include actions such as blocking the suspicious activity, sending an alert to system administrators, or even temporarily shutting down parts of the system to prevent a potential threat from causing damage. An IDPS offers several key cybersecurity benefits. It provides real-time threat detection, proactive threat prevention, improved network visibility and support for regulatory compliance.
There are several types of IDPS, each with specific features tailored to different environments. These include systems based on Network Behavior Analysis (NBA). This type of IDPS monitors network traffic flows to detect abnormal or suspicious behavior that could indicate an intrusion or attack. Based on behavior patterns, NBA systems can identify anomalies that would not be detected by traditional signature-based IDPS. They are particularly effective in detecting advanced threats and zero-day attacks that exploit unknown vulnerabilities.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF protects web applications by filtering and controlling HTTP and HTTPS traffic between web applications and the Internet. It can block malicious IP addresses identified by IDPS, offering additional protection against web-based attacks.In addition, a WAF can protect against web application-specific attacks, such as SQL injections and XSS attacks, which cannot be detected by a traditional IDPS.
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is a field of cybersecurity that focuses on the collection, analysis and distribution of information on potential and current threats to help make informed security decisions. CTI is essential for understanding the threat landscape, anticipating potential attacks and developing effective defense strategies.
CTI begins with the collection of data on potential threats. This data can come from a variety of sources, including security logs, network traffic flows, security incident reports, hacker forums, vulnerability bulletins and more. The data collected can include information on the tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers, indicators of compromise (IOCs), threat campaigns, threat actors, and so on.
Once the data has been collected, the next step is data analysis. This stage involves transforming the raw data into useful information. This may involve identifying patterns in the data, assessing the severity and credibility of threats, identifying vulnerabilities exploited by threats, and so on.
When integrated with a WAF and IDPS, Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) acts as an informant. Threat information provided by CTI can help the WAF to identify and block attacks targeting web applications. Similarly, IDPS can use CTI information to improve its detection of malicious behavior.
Security teams can use CTI information to understand the threat landscape and make informed decisions on how to manage threats and strengthen their defenses. In this way, CTI, by providing valuable threat intelligence, also bridges the gap between The Blocklist and tools to enhance the effectiveness of WAF and IDPS, and helps security teams to better protect their systems and data.
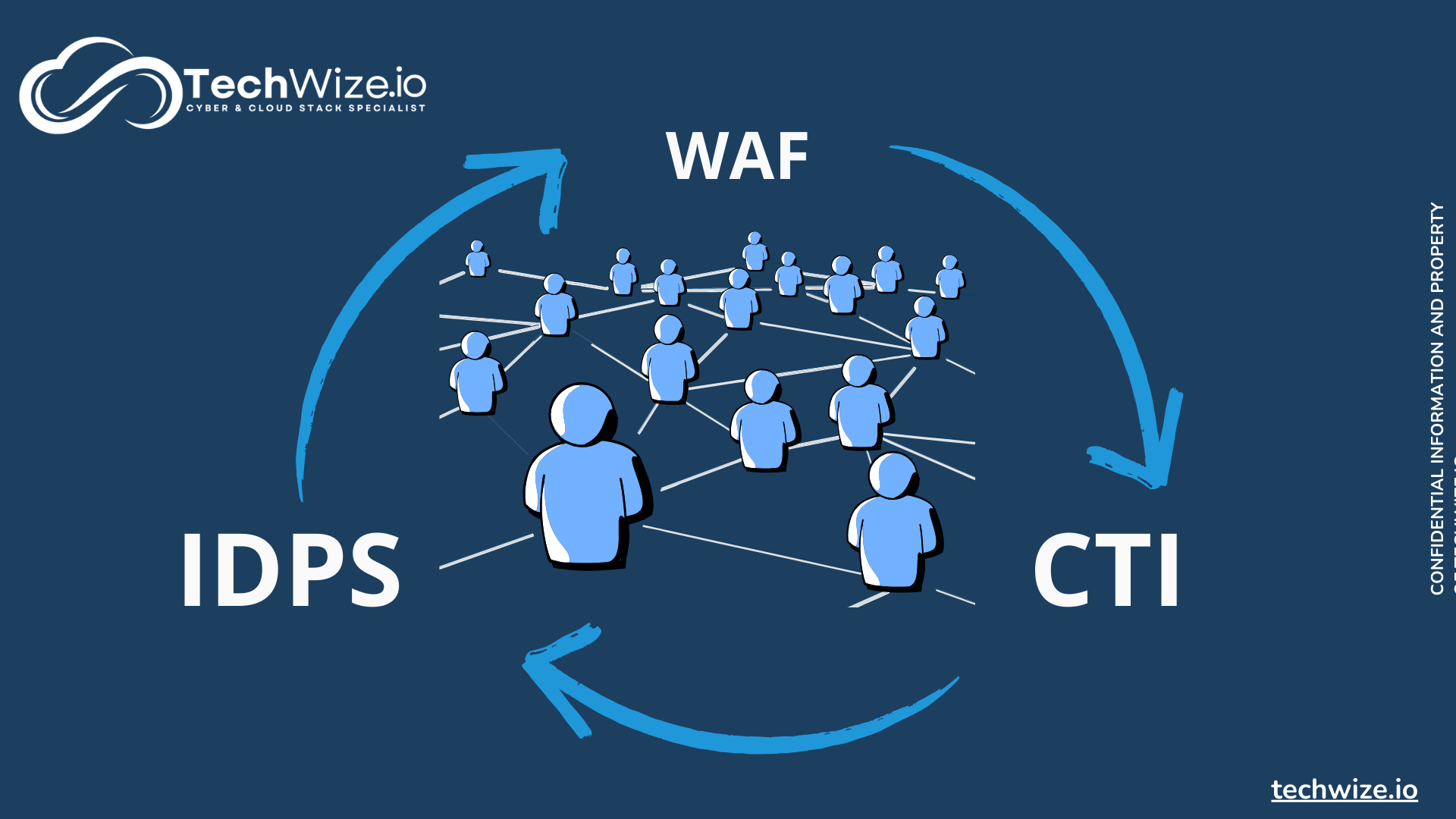
The interconnectivity of WAF, CTI and IDPS
These three components work together to provide robust protection against cyber threats. IDPS detects malicious behavior, WAF blocks malicious IP addresses identified by IDPS, and CTI enhances threat detection and reinforces the protection offered by WAF. Thanks to the collaborative approach, threat detection constantly improves as new data is shared by the community. This interconnectivity between WAF, CTI and IDPS is the strength of this collaborative, behavioral approach.
It makes it possible to respond to new challenges, notably by increasing threat detection and warning capacity, something that conventional WAFs could not do.
What’s more, this fusion reduces false positives and provides a better understanding of context. This in turn facilitates decision-making.
Traditional security solutions, such as network firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are not always sufficient to protect against modern attacks, particularly those targeting web applications. WAF offers additional protection against these attacks, while IDPS and CTI enhance threat detection and prevention. Above all, this increases the speed of detection and reaction.
Conclusion
A collaborative, behavioral approach has the potential to revolutionize the field of cybersecurity. By combining advanced behavior detection, effective blocking of malicious IP addresses and continuous improvement through community, we can create more robust and effective cybersecurity solutions to cyber threats. This approach offers comprehensive protection against cyber threats, while enabling rapid and accurate detection of new threats.
Collaboration and behavioral analysis represent the future of cybersecurity. We’re here to help you embrace this innovative approach and strengthen the security of your infrastructure and data.