In today’s digital world, cybersecurity has become a major concern for businesses and individuals alike. Protecting data transfers is essential to ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. This article explores the risks associated with data transfers, the types of cyber attacks that are common, and the advanced technologies used to secure them.
Data Transfers
Data transfers are ubiquitous in our daily digital lives. They include file sharing, online communications and financial transactions. These transfers are crucial to the operation of businesses and the privacy of individuals. However, they are also vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which makes it essential to secure them.
The risks of data transfers
Data transfers involve a number of major risks that can have devastating consequences for your business and your users. Data leakage is one of the most serious risks: if transfer mechanisms are not secure, sensitive information can be intercepted by unauthorised third parties. This can lead to breaches of confidentiality, considerable financial losses, and high costs associated with data recovery and ransoms demanded by attackers. For example, the average cost of a data breach in France is €3.84 million.
Data loss is another major risk. Data can be corrupted or lost during transfer, especially if it is sent via insecure platforms. This can cause service interruptions, productivity losses and delays in commercial operations, directly impacting business performance. In fact, 94% of companies that suffer a devastating data loss do not survive, and 51% go out of business within two years of the incident.
Reputational damage is an often underestimated but extremely damaging consequence. Companies that suffer data breaches can see their reputation tarnished, which can lead to a loss of trust from customers and partners. This loss of trust can have long-term repercussions on business relationships and loyalty.
Cyber attacks on data transfers can also have legal consequences. Companies can face legal action and fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations. The costs associated with these lawsuits and fines can be considerable and add further financial pressure to the business. For example, fines for non-compliance with the GDPR can reach up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s worldwide annual turnover, whichever is higher.
Cyber Attacks on Data Transfers
Cyber attacks on data transfers are varied and can have serious consequences. The most common attacks are :
Man-in-the-middle attack
In a Man-in-the-Middle attack, a cybercriminal intercepts and modifies communications between two parties without their knowledge. The attacker can read, insert and modify the messages exchanged, which can lead to the disclosure of sensitive data and unauthorised modifications of information. For example, during a financial transaction, an attacker could intercept the transaction details and modify them to redirect the funds to his own account.
Malicious code injection
Attackers can insert malicious code into data in transit, often via vulnerabilities in applications or transfer protocols. This malicious code can perform unauthorised actions, compromising the security of systems and data. For example, an attacker could insert a malicious script into a downloaded file, which, once opened, could infect the user’s system and allow unauthorised access.
Replay Attack
In a replay attack, attackers intercept data in transit and retransmit it later to create unauthorised actions. This can lead to fraudulent financial transactions or unauthorised access to systems. For example, an attacker could capture a legitimate bank transaction and replay it to transfer money repeatedly without the account owner’s permission.
Network sniffing
Network sniffing involves the use of tools to listen and capture data in transit over a network. Sensitive information, such as login credentials and personal data, can be stolen. For example, an attacker on a public Wi-Fi network could use a sniffing tool to intercept users’ login details and access their online accounts. Of course, attacks can be combined in many other ways.
New technologies
To counter these threats, advanced technologies are used to secure data transfers.
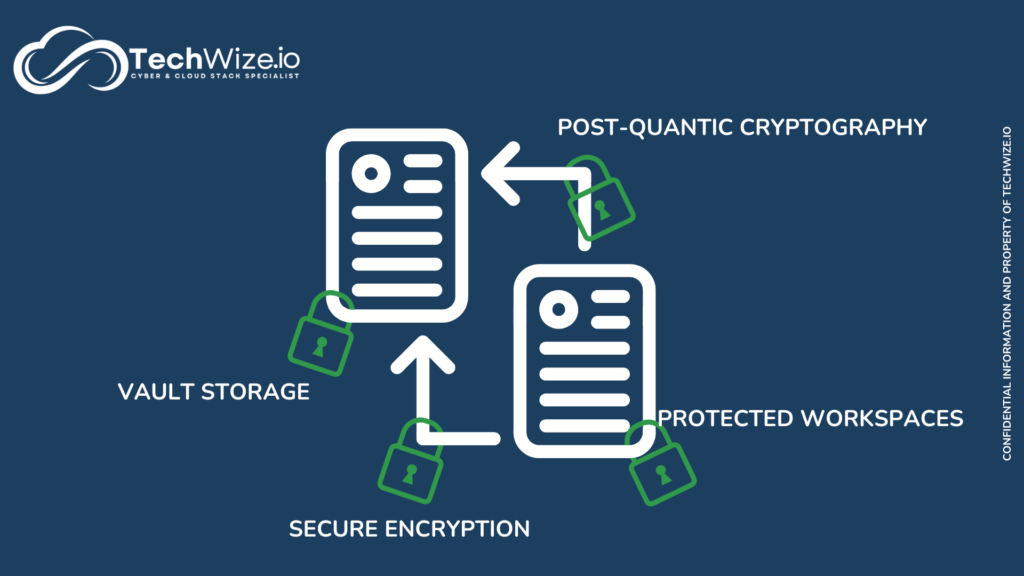
Post-quantum cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography is a cutting-edge technology designed to withstand attacks from future quantum computers, which could break current cryptographic systems. Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex mathematical problems in minutes, where a classical computer would take millennia.
This will make traditional cryptographic algorithms such as RSA and ECC obsolete. Post-quantum cryptography uses robust algorithms, such as those based on Euclidean networks or error-correcting codes, to guarantee long-term data security. These algorithms are designed to be resistant to both quantum and classical attacks, ensuring long-term protection of sensitive information.
Secure File Sharing
Secure file sharing solutions ensure the undeniable delivery of files, guaranteeing that they cannot be altered or denied by the sender. This protects the integrity of the information exchanged and ensures that files reach their recipient unaltered. These solutions use encryption techniques to secure files during transfer, as well as authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of senders and recipients. In addition, detailed transaction logs are often maintained to provide full traceability of file exchanges, which is crucial for security audits and regulatory compliance.
Vault storage
Sensitive data is stored in secure digital safes, protecting the information from unauthorised access. These safes use end-to-end encryption techniques to ensure that only authorised people can access the data. Digital safe systems also incorporate access management features, allowing administrators to define specific permissions for each user. This ensures long-term data confidentiality and security, even in the event of an intrusion attempt. In addition, digital safes often offer data backup and recovery options, ensuring that information remains accessible and protected against accidental loss.
Shared workspaces
Collaborative workspaces use strong signatures to guarantee the authenticity and integrity of shared documents. This enables secure and reliable collaboration between users, ensuring that every change made to documents is authenticated and traceable. Undeniable signatures use cryptographic techniques to link each modification to the identity of the user who made it, preventing any falsification or unauthorised alteration. These workspaces also offer version control capabilities, enabling users to track changes and revert to earlier versions if necessary. In addition, encryption mechanisms are used to protect documents during storage and transfer, ensuring complete end-to-end security.
Conclusion
Securing data transfers is essential to protect sensitive information from cyber-attacks. Using advanced post-quantum cryptography technology, this enables secure file sharing, vault storage, shared workspaces and more, in an enhanced environment for businesses. Their cybersecurity reaches a level of protection never achieved before. They can now guard against emerging threats posed by evolving technologies and attack methods.
By adopting post-quantum cryptography with its robust security measures, businesses can protect their sensitive communications and information while maintaining the trust of their employees and partners. Techwize.io is an exclusive reseller of this technology. Please do not hesitate to contact us.